Contributing pigmentation is a key concept in hair coloring, particularly in understanding how to create desired tones and make color corrections. This term refers to the underlying natural pigment within the hair shaft that influences the final color outcome when dye is applied.
Natural Contributing Pigments
Natural hair color contains pigments that vary in levels and tones depending on the individual’s natural hair color level:
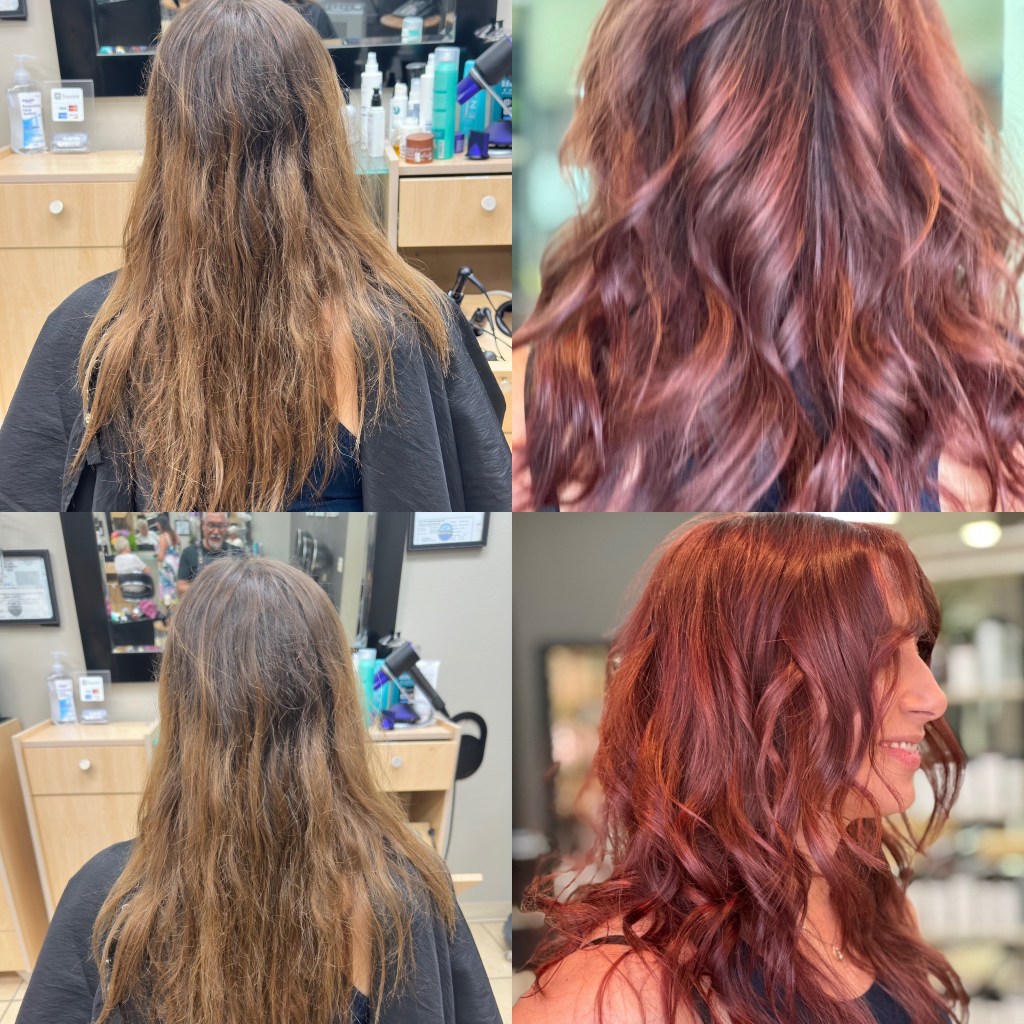
• Dark hair (levels 1-4) has a high concentration of eumelanin, resulting in underlying tones of deep red or dark orange.
• Medium hair (levels 5-7) contains a balance of eumelanin and pheomelanin, with underlying pigments in the range of orange and yellow.
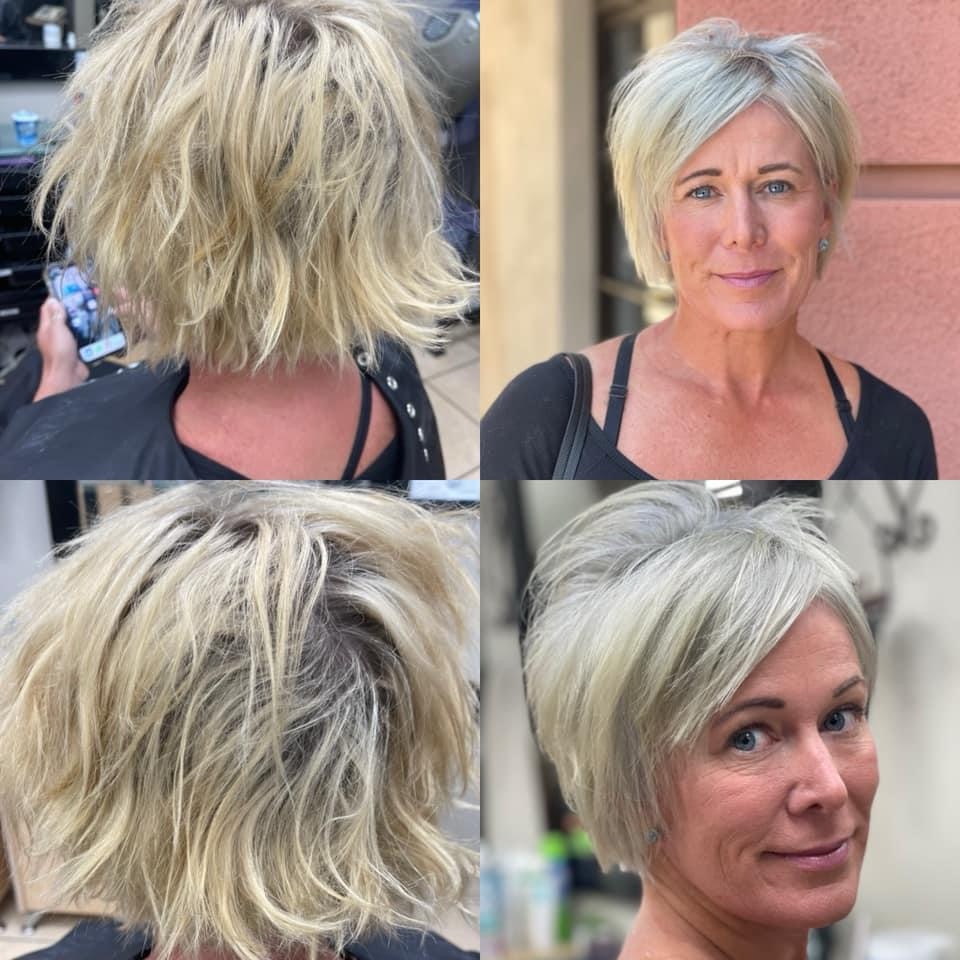
• Light hair (levels 8-10) has lower melanin concentration, often leading to underlying pale yellow tones.
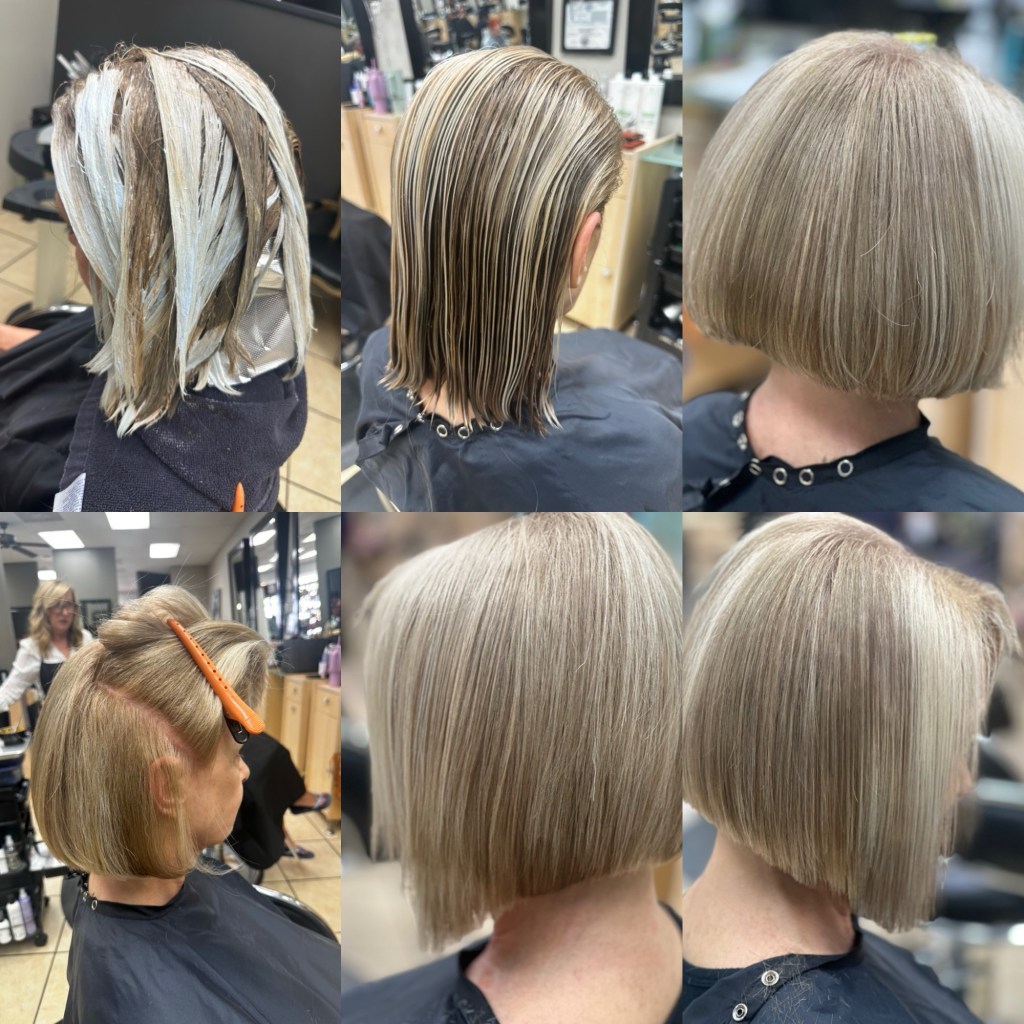
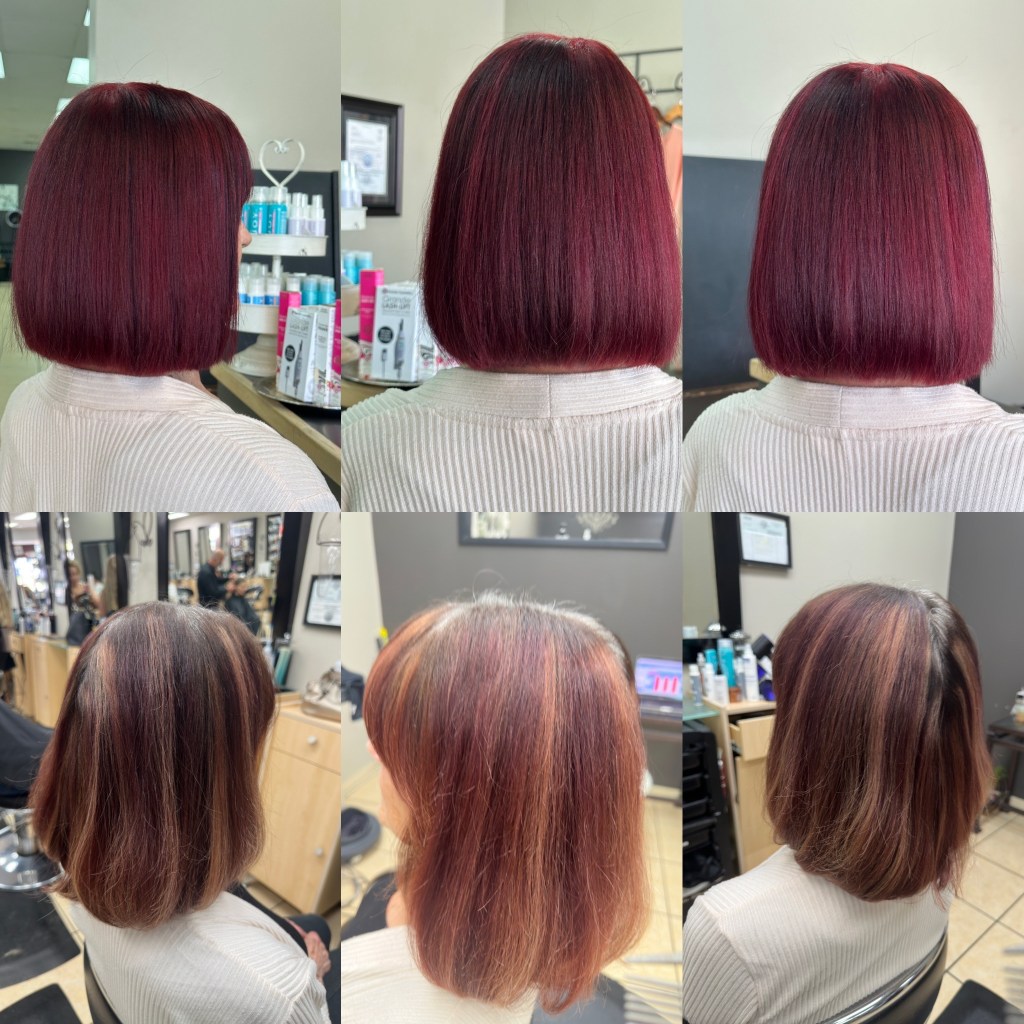
When lightening hair, the process removes some of the natural pigments, exposing the underlying tones. For example, lifting dark hair often brings out warm red or orange undertones. Understanding these tones allows colorists to make informed decisions on how to counterbalance or enhance them with artificial pigments to achieve the desired result.
Role in Hair Color Correction
In corrective coloring, contributing pigments are crucial to addressing issues such as unwanted brassy tones, uneven coloring, or color fade. For instance, if a client’s hair has underlying orange tones after lightening, the colorist may apply a blue-based toner to neutralize the warmth and achieve a cooler result.
In cases where color needs to be intensified, contributing pigmentation helps guide the selection of shades that will blend well with the client’s natural undertones. This ensures that the color remains vibrant and harmonious with the client’s original pigment structure.
Enhancing Contributing Pigments for Customized Shades
When creating custom shades, contributing pigments can enhance the richness and dimension of color. By working with these natural undertones, colorists can craft a more personalized color that reflects depth and luminosity. For instance, adding a violet hue to hair with a yellow undertone can create a rich beige or pearl blonde, blending cool and warm tones seamlessly.
In summary, a deep understanding of contributing pigmentation allows colorists to predict how hair will respond to color processes and make adjustments accordingly. This knowledge is essential for both achieving desired shades and correcting unwanted tones, ensuring beautiful, balanced, and long-lasting color results.

























Leave a comment